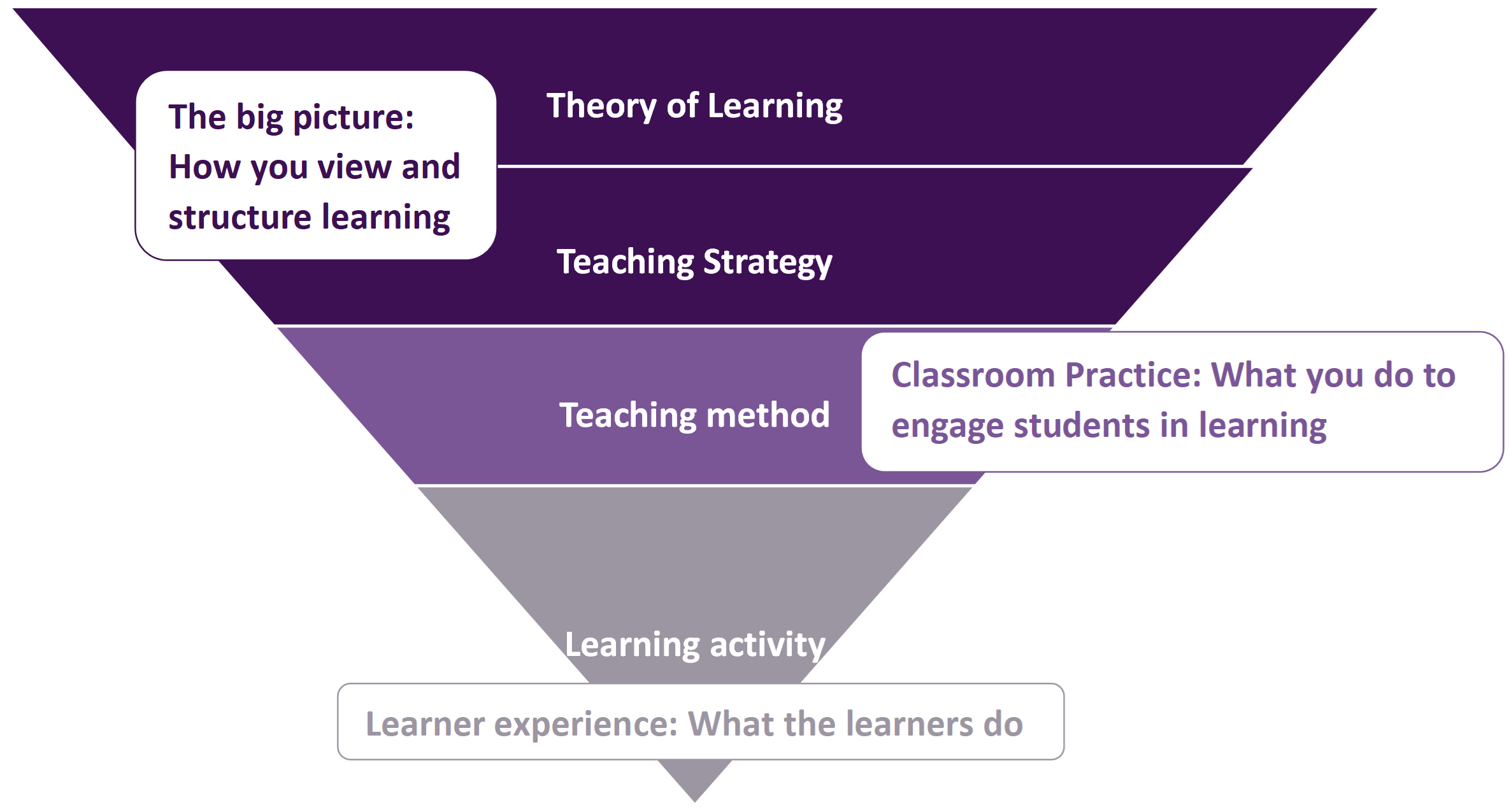
Problem-based learning (PBL) is a teaching strategy that involves learners working on real-life problems in small groups. PBL can be applied systematically across whole programmes in particular modules or units (Barrett & Moore, 2010a). Barrett and Moore (2010a) conceptualise PBL as having six interrelated elements.
|
PBL problem design |
Features of the PBL problem design:
|
|
PBL tutorials in small teams |
A key element of PBL is the use of small teams:
|
|
PBL compatible assessment |
PBL as a teaching strategy incorporates assessment design. Assessments need to align with a problem-based learning process. PBL assessment should incorporate the following elements:
|
|
PBL curriculum development |
A PBL curriculum is founded on learners working to solve problems in small teams, this process is supported by other curriculum inputs, such as lectures and practice placements. |
|
Developing knowledge and capabilities |
PBL enables students to learn concepts by working on problems designed around these concepts. In addition to knowledge PBL aims to develop other skills including:
|
|
Philosophy of problem-based learning |
PBL enables deeper consideration of what learning is, the purpose of higher education. |
(Source: Barrett & Moore, 2010a; Barrett & Moore, 2010b; Pettigrew, Scholten & Gleeson, 2010)